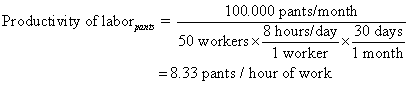Useful definitions related to productivity
There are some terms that are frequently used when we are talking about productivity or methods of performance measurement. These terms are the following:
- Productivity;
- Total factor productivity;
- Production frontier;
- Technical efficiency;
- Feasible production set.
The definition of productivityWe can define productivity of a firm as the ratio of the output that it produces to the input that it uses.When the product process involves a single input and a single output, productivity can be found easily. However, when there is more than one input, which is often the case, then a method for aggregating these inputs into a single index of inputs must be used to obtain a ratio measure of productivity.Total factor productivityWhen we are talking about productivity, generally we are referring to total factor productivity, which is a productivity measure that involves all factors of production. Other measures of productivity, such as labor productivity, fuel productivity and land productivity, are often called partial measures of productivity. These partial productivity measures can provide a misleading indication of overall productivity when considered isolated.Production frontierProduction frontier may be used to define the relationship between the input and the output. The production frontier represents the maximum output attainable from each input level.Technical efficiencyWhen firms operate in the production frontier they are technically efficient.Feasible production setIt is the set of all input-output combinations that are feasible. This set consists of all points below the production frontier. The points along the production frontier define the efficient subset of this feasible production set.
Productivity
and performance measurement
Productivity
is concerned with measuring the performance of firms, which convert
inputs into outputs. An example of a firm is a computer factory that
uses material, labor and capital (inputs) to produce computers
(output). The performance of this kind of factory can be defined in
some ways. For example a basic measure of performance is a
productivity ratio.
What
is a productivity ratio?
It
is the ratio of outputs to inputs, where larger values of this ratio
are associated with better performance.
Note
that performance is a relative concept, because for example, the
performance of the factory in 2021 can be measured relative to its
2020 performance, or 2019, or 2010, etc.
The
methods of performance measurement can be applied to a variety of
firms or “decision making unit”, as can be named in some of the
literature on productivity and efficiency analysis. They can be
applied to private sectors firms producing goods or to service
industries. The methods may also be used by a particular firm to
analyze the relative performance of units within the firm or to
measure the performance in non-profit organizations.
Even
the context of productivity analysis mentioned above involve
micro-level data, the methods can be used for making performance
comparisons at higher levels of aggregation, like the performance of
an industry over time or across geographical regions, and so on and
so forth.
The
methods of performance measurement differ according to the type of
measures they produce, the data they require and the assumptions they
make regarding the structure of the production technology and the
economic behavior of decision makers.
What
are the requirements for performance measurement?
Some
methods only require data on quantities of inputs and outputs while
other methods also require price data and various behavioral
assumptions, such as cost minimization, profit maximization, etc.
What is the importance of productivity and how to improve it
Creating goods and services in different areas requires that certain
resources be transformed into these (raw materials, supplies, labor,
etc.). The more efficiently the mentioned transformation happens, the
more productive it will be.
In its most basic form, productivity can be understood as the
proportion of outputs (goods and services) among the inputs
(resources such as raw materials, inputs, labor, capital, etc.).
Improving productivity it is of vital importance for any company.
Improving the ratio of outputs and inputs (productivity) will be one
of the most important tasks (if not the most important) that
industrial engineering and in general the directors of operations or
production face in their daily work.
How to improve productivity?
Productivity improvement can be achieved in the following ways:
either by reducing the inputs while the outputs are kept constant, by
increasing the outputs while the inputs are kept constant, or by
increasing the outputs and reducing the inputs at the same time. This
implies an increase in productivity.
From the economic perspective, the inputs can be identified as land,
labor, capital and management. These inputs are combined in a
production system. Through management, the conversion of inputs into
outputs can be achieved. The better the management the greater the
productivity that can be achieved in a given production system.
The outputs resulting from a production process can be goods or
services of various kinds (for example computers, calculators, cell
phones, soft drinks, education, hotels, etc.). Production then can be
viewed as all the goods and services produced. The fact of having a
high production may originate from an increasing number of people
working (which can lead to an increase in employment levels), however
this situation does not necessarily imply that there is a high
productivity.
Measuring productivity is a good way to assess a country's ability to
provide and improve the living standards of its inhabitants. The
increase in productivity is closely linked with the improvement in
productive capacity and therefore, in a macro context, it can lead to
an improvement in the standard of living.
Without an increase in productivity, the increase in the benefits
generated by the factors of production (labor, capital, land,
technology, management) implies an increase in prices. Conversely,
when productivity increases, prices tend to decrease since more is
produced with the same amount of resources.
What
is productivity? How to measure and calculate it?
In
general terms productivity can be defined as the relationship between
outputs and inputs.
In
which sectors can be applied the definition of productivity?
This
definition of productivity is generic and applies in an enterprise, a
sector of economic activity or the economy as a whole. Productivity
can be used to asses or measure how much output can be extracted from
a given input.
What
is the mathematical representation of productivity?
Mathematically
productivity may be expressed by.
Example
of how to calculate productivity
A
textile factory works eight hours per day manufacturing 100.000 pants
and 50.000 sweaters a month using 110000 and 75000 square meters of
polyester cloth, respectively. If the pants section of the factory
has 50 workers and the sweaters section 75, we can calculate the
productivity as follow:
Measure
of materials productivity
According
to the formula given before, the materials productivity may be
measured as the relation between the quantity of finished products
and the materials used in the process.
Therefore,
the productivity for the pants and sweaters lines of the factory are:
Measure
of labor productivity
The
labor productivity may be measured as the relation between the
quantity of finished products and the labor hours used in the
process.
Therefore,
the productivity for the pants and sweaters lines of the factory are:
The
productivity of any factor of production or input, can be measured in
the form we exemplify before.
Productivity and industrial engineering
What
is productivity?
Applied
in an enterprise, a sector of economic activity or the economy as a
whole, productivity may be defined as an output and input relation.
The
term productivity can be used to asses or measure the extent to which
a certain output can be extracted from a given input. This may
appears simple enough in cases where both the output and the input
are tangible and can be easily measured; however, in cases where
intangibles are introduced measure of productivity can be more
difficult.
Calculation
of productivity
Productivity
can be calculated as follows:
Productivity
and industrial engineering in goods production
In
the case of goods production, the objective is the manufacturing to a
better cost, through the raw material, with productivity of the
primary resources of production: Materials, human resources and
machines. It's on these, where the action of industrial engineers
should address their efforts. Increasing productivity indexes and
reducing production costs, are fundamental tasks of an industrial
engineer.
Productivity, types of productivity, productivity index, total productivity
Whats is productivity?
Productivity is the ratio of output to some or all of the resources used to produce the output.
Types of productivity
We can mention the following types of partial productivities:
- Labor productivity: units produced / hours worked
- Capital productivity: output / capital input
- Material productivity: output /material input
What is the productivity index?
We can calculate a type of partial productivity as labor productivity as output per man hours for a complete year. These figures obtained from year to year can be indexed and can be related to a base year so that output per man our comparisons can be made.
Definition of total productivity
It is the ratio of tangible output and tangible input.
Differences among partial productivity, total factor productivity and total productivity
Men, materials, machines, methods, money, energy, etc. are inputs.
- Partial productivity: output / one class of input
- Total factor productivity: net output / (labor + capital)
- Total productivity : sum of all tangible outputs / sum of all tangible inputs